Waste Hierarchy and Stages of Circularity

Connor Hill
15 years: Circular economy strategist
In this video, Connor Hill continues discussing the circular economy and explains the waste hierarchy and the 8 stages of circularity.
In this video, Connor Hill continues discussing the circular economy and explains the waste hierarchy and the 8 stages of circularity.

Waste Hierarchy and Stages of Circularity
16 mins 25 secs
Key learning objectives:
Understand the role of the circular economy in addressing overconsumption and resource depletion
Understand the waste hierarchy triangle
Understand the 8 different stages of circular economy
Overview:
The circular economy aims to reduce overconsumption and resource depletion by promoting the reuse, repair, and recycling of products and materials. In order to transition to a circular economy, it is very important to consider our consumption habits and the lifecycle of products. This can be illustrated using the waste hierarchy triangle and the 8 stages of circularity. It is the collective responsibility of companies, communities, and governments to help achieve this transition.
How can the circular economy be a solution to the overproduction and consumption model?
The circular economy is a system that aims to move products and materials from point A to point B and then back to point A, enabling their repeated use and reducing the reliance on virgin resources - unlike the current linear economy which has led us to this point of overproduction and consumption.
What are the two perspectives of the circular economy?
Circle of life : How organic matter is returned to the biological cycle through the nutrient cycle, contributing to soil fertility and ecosystem health.
Circle of stuff : Refers to human-made products and the challenges associated with their disposal
What is the waste hierarchy?
The waste hierarchy is introduced as a framework for prioritising waste management strategies. Refusing unnecessary consumption and reusing existing products are presented as the first steps. Refurbishing and repairing products are encouraged, followed by reselling and only as a last resort, recycling. Landfill and incineration are discouraged due to the loss of materials from the circular value chain.
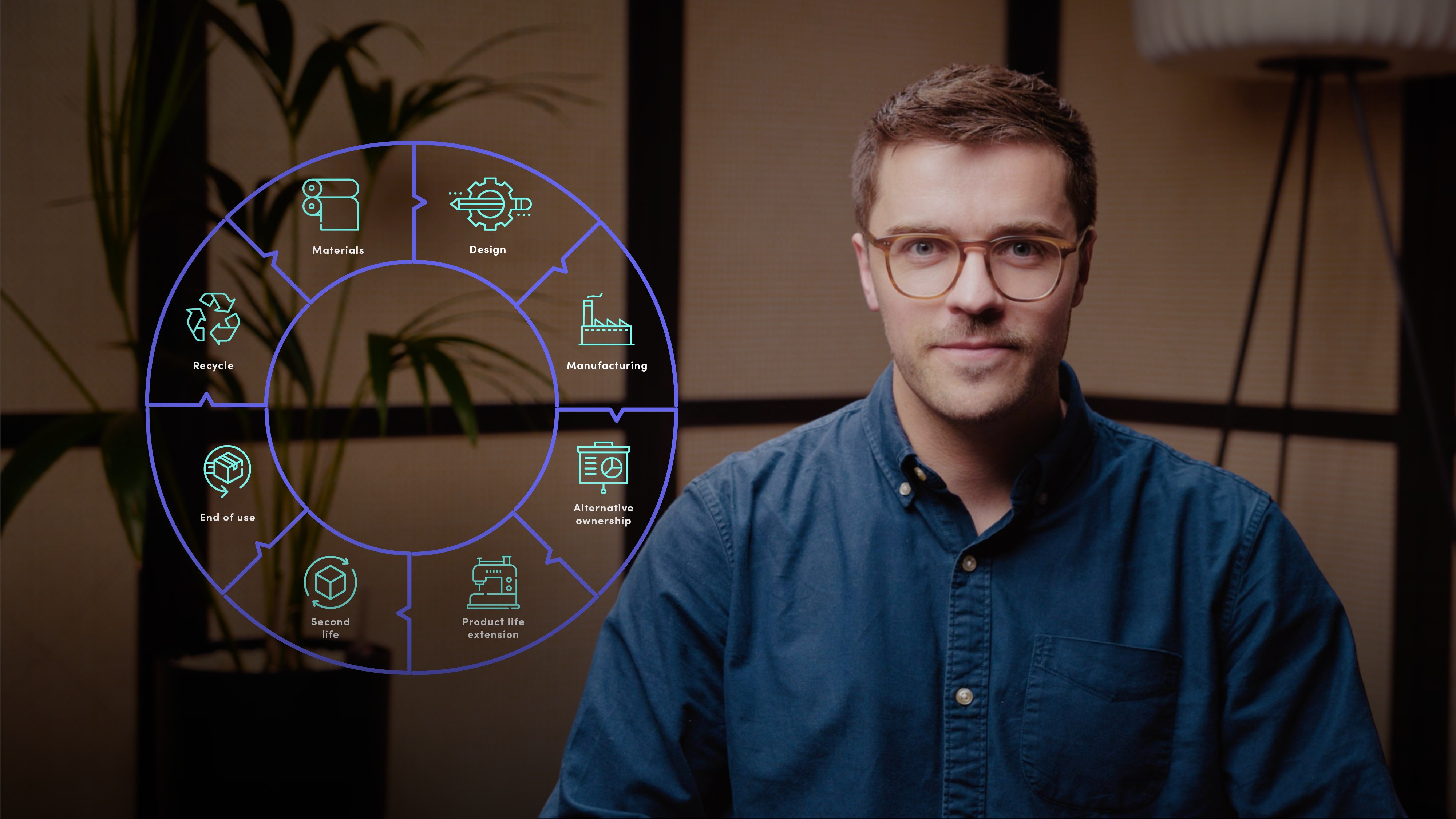
What are the 8 stages of circularity?
- Materials: Start with recycled or renewable materials, reducing dependence on virgin resources and considering sustainable sourcing practices.
- Design: Create timeless and durable products that are modular, upgradable, and resistant to becoming obsolete.
- Manufacturing: Implement zero-waste design and manufacturing processes to minimise waste in the supply chain.
- Alternative Ownership Models: Explore rental or subscription services that shift the focus from ownership to accessibility (multiple uses of the same product)
- Product Life Extension: Offer services like lifetime warranties and repair options to prolong the use of products.
- Resale: Facilitate easy resale channels for customers, promoting the circulation of products and reducing the need for new production.
- End of Use/Collection: Establish mechanisms for the proper collection and disposal of products at the end of their life, including curbside.
- Recycling/second generation: Recycle materials efficiently and reduce the dependence on extracting virgin materials and promote a more sustainable circular economy.

Connor Hill
There are no available Videos from "Connor Hill"